tree in bud opacities seen in
TIB opacities can be seen in isolation bronchiolitis 1314 or with other infl ammatory imaging fi ndings includ-. Turn on spectral and notice that the tree-in-bud opacities have clear iodine uptake.
This is very hard to pick up on imaging or prove histologically as this is well beyond the range of bronchoscopy.
. This is consistent with intrabronchial tumor. Ad Get a brief easy to understand overview of the common signs of lung cancer. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Originally reported in cases of endobronchial spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis this. Where there is small airways disease and tree in bud is present this can be termed an exudative bronchiolitis. What are tree-in-bud opacities and inwhat conditions may they be seen.
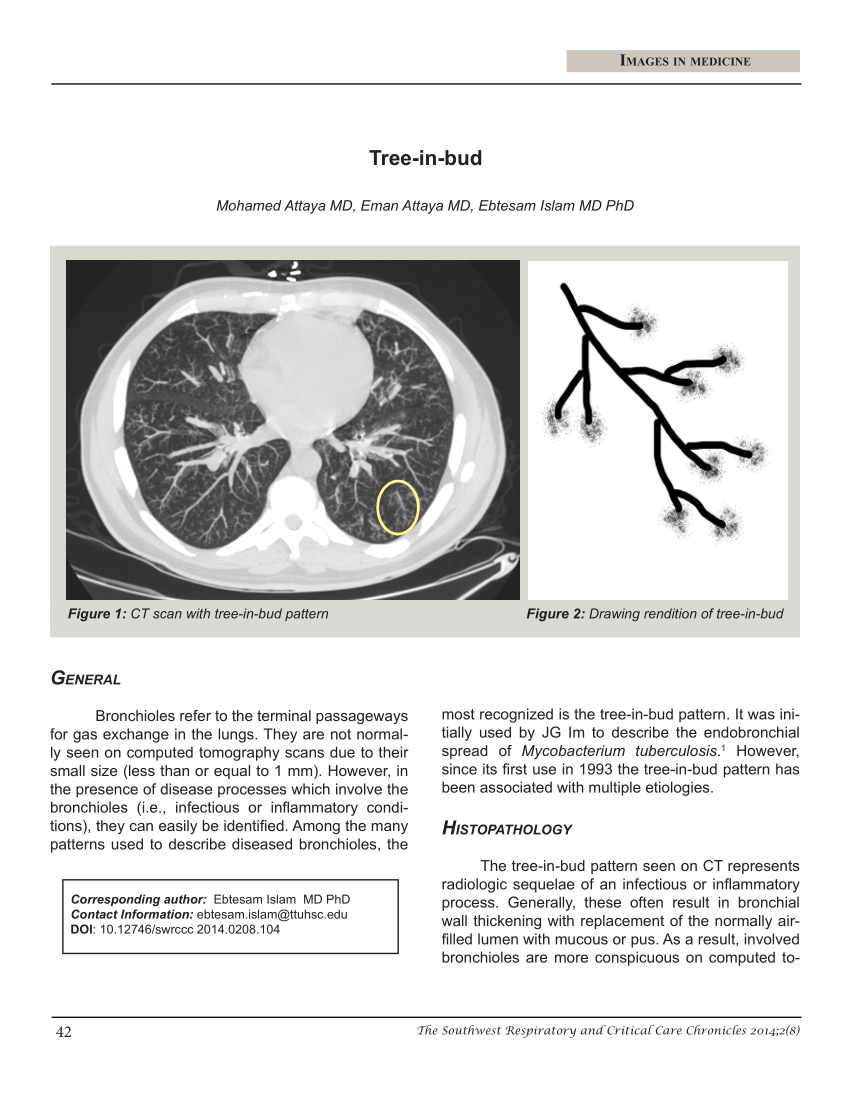
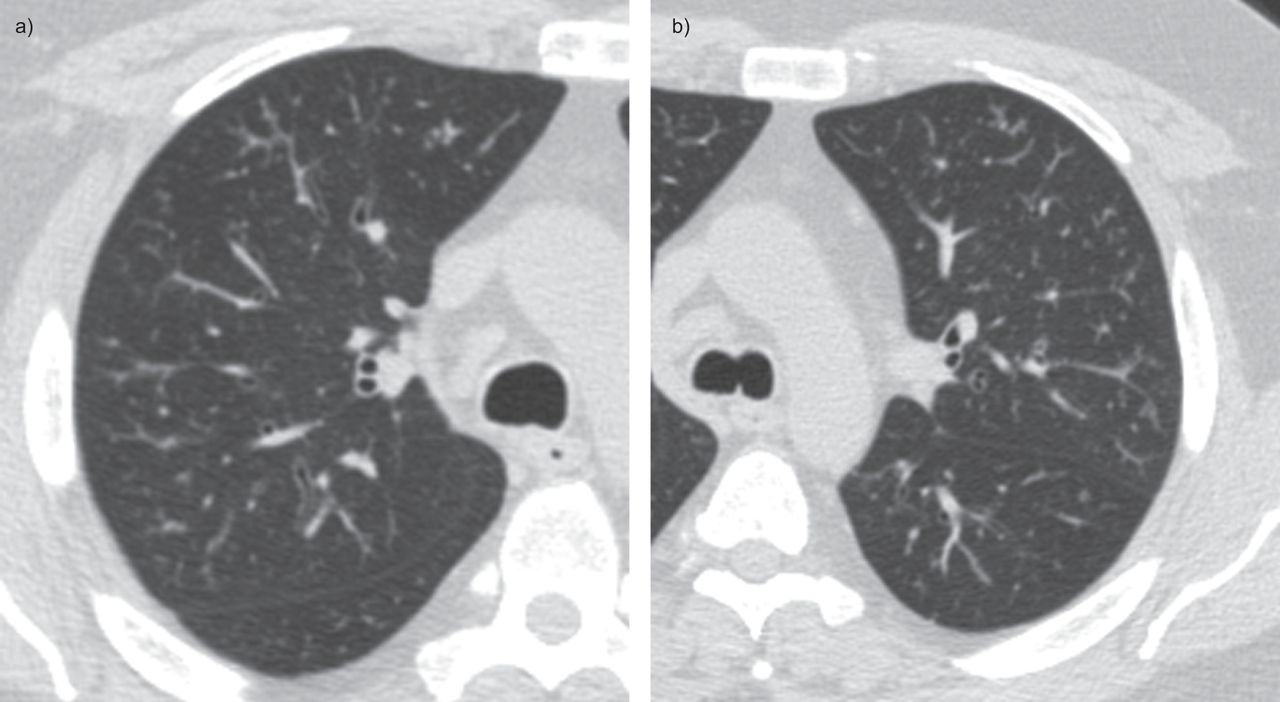
Tree-in-bud opacities appear as tiny centrilobular branching structures on CT most often in the lung periphery which resemble budding trees Figure 18-4. Patient does have a large para-esophageal lymph node as. Diffuse panbronchiolitis is an exudative bronchiolitis.
The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. As you can see the possible causes of a tree in bud appearance are legion. These are due to filling of the distal bronchioles and involvement of the adjacent alveoli most often caused by infectious bronchiolitis bronchitis and aspiration.
It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk. Patient does not complain of cough. It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk.
Get the Latest On The First Signs of Lung Cancer In This Article. What causes tree-in-bud opacities. Reminiscent of a tree in bud in the spring Representing.
1 refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Fig. Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of.
The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. Dilated terminal bronchioles with impacted mucus that are often seen in atypical mycobacterial infections andaspiration but may also be seen in bacterial or viralinfections collagen vascular disease fungal infections collagen diseases CF or toxic.
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles
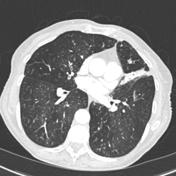
Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
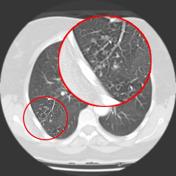
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Hrct Scan Of The Chest Showing Diffuse Micronodules And Tree In Bud Download Scientific Diagram

Computed Tomography Of The Chest Showed Nodular Opacities With Tree In Download Scientific Diagram

Ct Scan Of Chest Revealing Scattered Tree In Bud Opacities In Both Download Scientific Diagram
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
Hypereosinophilic Obliterative Bronchiolitis A Distinct Unrecognised Syndrome European Respiratory Society
